팩토리 메서드 패턴(Factory Method Pattern)
팩토리 패턴이란?
객체의 생성을 캡슐화하는 패턴입니다. 구체적인 객체의 생성 과정을 팩토리로 모듈화하여 구체적인 부분이 아닌 추상적인 부분에 의존할 수 있도록 합니다.
팩토리 패턴에는 팩토리 메서드 패턴과 추상 팩토리 패턴이 있습니다.
| Pattern | 공통점 | 차이점 |
|---|---|---|
| 팩토리 메소드 패턴 | 객체의 생성부를 캡슐화하여 결합을 느슨하게 합니다. 구체적인 타입에 의존하지 않도록 합니다. | 상속을 통해 서브 클래스에서 팩토리 메소드를 오버라이딩하여 객체의 생성부를 구현 |
| 추상 팩토리 패턴 | 객체의 집합을 생성하기 위한 정의를 추상체에 위치시키고 하위의 구현체에서 세부적인 집합 생성 과정을 구현 (Fatory Method를 이용해 구현) |
# 팩토리 메서드 패턴(Factory Method Pattern)이란?
GoF 디자인 패턴 중 생성 패턴(Creational Pattern) 중 하나입니다. 다양한 구현체(Product)가 있고, 그 중에서 특정한 구현체를 만들 수 있는 다양한 팩토리(Creator)를 제공할 수 있습니다. 상속을 통해 서브 클래스에서 팩토리 메서드를 오버라이딩하여 객체의 생성부를 구현합니다.
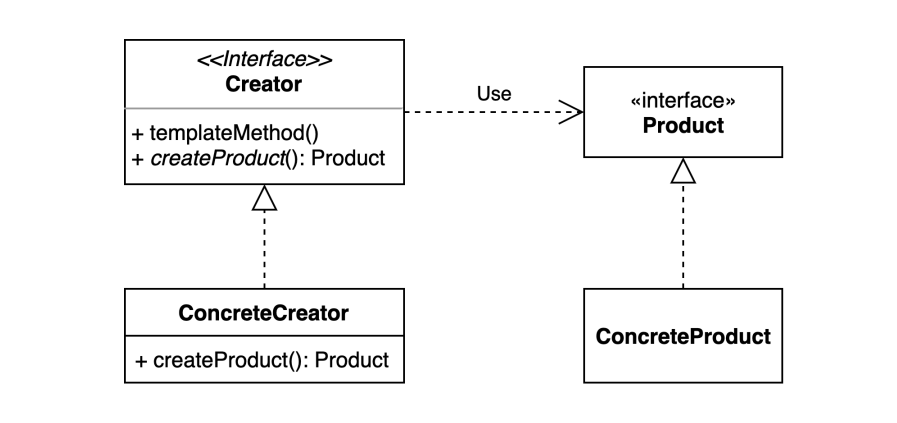
사용 이유
객체를 생성하기 위해 인터페이스를 정의하지만, 어떤 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성할지에 대한 결정은 서브클래스에서 이루어지도록 하여 재정의 가능한 것으로 설계 하지만, 복잡해지지 않게 합니다.
- 생성할 객체 타입을 예측할 수 없을 때
- 생성할 객체를 기술하는 책임을 서브클래스에게 정의하고자 할 때
- 객체 생성의 책임을 서브클래스에 위임시키고 서브클래스에 대한 정보를 은닉하고자 할 때
장점
- 기존 코드(인스턴스를 만드는 과정)를 수정하지 않고 새로운 인스턴스를 다른 방법으로 생성하도록 확장할 수 있습니다.
- Product와 Creator 간의 결합이 느슨해집니다.
- OCP를 적용했기에 가능
- 코드가 간결해집니다.
단점
- 클래스가 많아집니다.(클래스 계층도 커질 수 있습니다.)
- 제품 클래스가 바뀔 때마다 새로운 서브 클래스를 생성해야 합니다.
참고사항
- 자바8
- 인터페이스에 추상 메서드가 아닌 default 메서드를 통해 기능 구현이 가능해져서 상속을 받는 서브 클래스의 중복 코드를 제거할 수 있습니다.
- 자바 9
- 기능 구현이 가능해지며 private 메서드로 가독성 좋게 메서드 분리하여 작성할 수 있습니다.
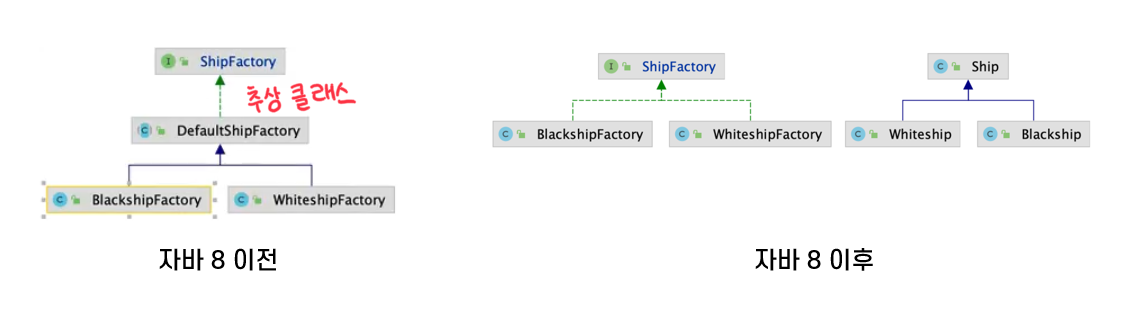
예시
단순한 버전
@Getter
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class EspressoBean {
private String beanName;
private final int amount;
public EspressoBean(String beanName, int amount) {
this.beanName = beanName;
this.amount = amount;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public boolean isValid() {
return Strings.isBlank(beanName) || amount < 1;
}
}
@Getter
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Coffee {
private final EspressoBean espressoBeans;
private final int waterAmount;
private String name;
public Coffee(EspressoBean espressoBeans, int waterAmount) {
this(espressoBeans, waterAmount, null);
}
public Coffee(EspressoBean espressoBeans, int waterAmount, String name) {
this.espressoBeans = espressoBeans;
this.waterAmount = waterAmount;
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/**
* Factory에서 담당해야할 기능은 주문을 받는 기능과 그와 관련된 부가기능 뿐이다.
*/
public class CoffeeMachine {
private CoffeeMachine() {
}
public static Coffee orderCoffee(EspressoBean espressoBean, int water, String name) {
// 유효성 검사
if (espressoBean.isValid()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("원두가 부족합니다.");
}
if (isWaterAmount(water)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("물이 부족합니다.");
}
prepareFor(espressoBean);
// 원두 분쇄 작업
espressoBean.setBeanName("분쇄된 " + espressoBean.getBeanName());
Coffee coffee = new Coffee(espressoBean, water);
if (water == 0) {
coffee.setName("에스프레소 커피");
} else {
coffee.setName("아메리카노 커피");
}
servingTo(name, coffee);
return coffee;
}
private static boolean isWaterAmount(int water) {
return water < 1;
}
private static void prepareFor(EspressoBean espressoBean) {
System.out.println("커피 제조중...");
System.out.println("사용한 원두는 " + espressoBean.getBeanName() + " 입니다.");
}
private static void servingTo(String name, Coffee coffee) {
System.out.println(name + " 님 주문하신 " + coffee.getName() + " 나왔습니다.");
}
}
복잡한 버전
@Getter
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class EspressoBean {
private String beanName;
private final int amount;
public EspressoBean(String beanName, int amount) {
this.beanName = beanName;
this.amount = amount;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public boolean isValid() {
return Strings.isBlank(beanName) || amount < 1;
}
}
@Getter
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Coffee {
private final EspressoBean espressoBeans;
private final int waterAmount;
private String name;
public Coffee(EspressoBean espressoBeans, int waterAmount) {
this(espressoBeans, waterAmount, null);
}
public Coffee(EspressoBean espressoBeans, int waterAmount, String name) {
this.espressoBeans = espressoBeans;
this.waterAmount = waterAmount;
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
public class Americano extends Coffee {
public Americano(EspressoBean espressoBeans, int waterAmount) {
super(espressoBeans, waterAmount, "아메리카노 커피");
}
}
public class Espresso extends Coffee {
public Espresso(EspressoBean espressoBeans, int waterAmount) {
super(espressoBeans, waterAmount, "에소프레소 커피");
}
}
public interface CoffeeMachine {
default Coffee orderCoffee(EspressoBean bean, int water, String orderName) {
validateBean(bean);
validateWaterAmount(water);
Coffee coffee = createCoffee(bean, water);
servingTo(orderName, coffee);
return coffee;
}
Coffee createCoffee(EspressoBean bean, int water);
private void validateBean(EspressoBean bean) {
if (bean.isValid()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("원두가 부족합니다.");
}
}
private void validateWaterAmount(int water) {
if (water < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("물이 부족합니다.");
}
}
private void prepareFor(String espressoBean) {
System.out.println("커피 제조중...");
System.out.println("사용한 원두는 " + espressoBean + " 입니다.");
}
private void servingTo(String name, Coffee coffee) {
System.out.println(name + " 님 주문하신 " + coffee.getName() + " 나왔습니다.");
}
}
public class AmericanoFactory implements CoffeeMachine {
@Override
public Coffee createCoffee(EspressoBean bean, int water) {
EspressoBean grindBean = grindBean(bean);
return new Americano(grindBean, 10);
}
private EspressoBean grindBean(EspressoBean espressoBean) {
espressoBean.setBeanName("갈린 " + espressoBean.getBeanName());
return espressoBean;
}
}
public class EspressoFactory implements CoffeeMachine {
@Override
public Coffee createCoffee(EspressoBean bean, int water) {
EspressoBean grindBean = grindBean(bean);
return new Americano(grindBean, 0);
}
private EspressoBean grindBean(EspressoBean espressoBean) {
espressoBean.setBeanName("갈린 " + espressoBean.getBeanName());
return espressoBean;
}
}
결론
팩토리 메서드 패턴을 통해 클래스 간의 결합도를 낮출 수 있습니다. 직접 객체를 생성해 사용하는 것을 방지하고 서브 클래스에 위임함으로써 효율적으로 코드 제어를 할 수 있고 의존성을 제거하며 결합도를 낮출 수 있습니다.
reference
댓글남기기