[Spring] Spring Security란?
Spring Security
Spring Security란 Spring 기반의 애플리케이션의 보안(인증과 권한, 인가) 를 담당하는 스프링 하위 프레임워크입니다. Spring Security 는 인증과 권한에 대한 부분을 Filter 로 처리하고 있습니다.
인증(Authentication)과 인가(Authorization)
- 인증(Authentication) : 해당 사용자가 본인이 맞는지 확인하는 절차
- 인가(Authorization) : 인증된 사용자가 요청한 자원에 접근 가능한지 결정하는 절차 (인증에 성공한 후 인가)
Spring Security는 인증 절차를 거친 후 인가 절차를 진행하며 인가 과정에서 해당 리소스에 대한 접근권한이 있는지 확인합니다. Spring Security 는 이러한 인증과 인가를 위해 Principal 를 아이디로, Credential 을 비밀번호로 사용하는 Credential 기반의 인증방식을 사용합니다.
- Principal(접근 주체) : 보호받는 리소스에 접근하는 대상
- Credential(비밀번호) : 리소스에 접근하는 대상의 비밀번호
Spring Security 모듈
SecurityContextHolder
보안 주체의 세부 정보를 포함하여 응용프로그램의 현재 SecurityContext 에 대한 세부 정보가 저장됩니다. SecurityContextHolder 는 기본적으로 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 방법과SecurityContextHolder.MODE_THREADLOCAL 방법을 제공합니다.
SecurityContext
Authentication 을 보관하는 역할을 합니다. SecurityContext를 통해서 Authentication 객체를 꺼내올 수 있습니다.
Authentication
현재 접근하는 주체의 정보와 권한을 담는 인터페이스 입니다. Authentication객체는 SecurityContext 에 저장되며, SecurityContextHolder -> SecurityContext -> Authentication 순으로 접근할 수 있습니다.
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
// 현재 사용자의 권한 목록을 가져옴
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// credentials(주로 비밀번호)을 가져옴
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
// Principal 객체를 가져옴.
Object getPrincipal();
// 인증 여부를 가져옴
boolean isAuthenticated();
// 인증 여부를 설정함
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
Authentication 인터페이스를 구현한 AbstractAuthenticationToken 의 하위 클래스로, User 의 ID가 Principal 역할을 하고, password 가 Credential 의 역할을 합니다. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken의 첫 번째 생성자는 인증 전의 객체를 생성하고, 두 번째 생성자는 인증이 완료된 객체를 생성합니다.
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
// 주로 사용자의 ID에 해당함
private final Object principal;
// 주로 사용자의 PW에 해당함
private Object credentials;
// 인증 완료 전의 객체 생성
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) {
super(null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
// 인증 완료 후의 객체 생성
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true); // must use super, as we override
}
}
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationToken implements Authentication, CredentialsContainer {
}
AuthenticationProvider
실제 인증에 대한 부분을 처리하는 부분입니다. 인증 전의 Authentication 객체를 받아서 인증이 완료된 객체를 반환하는 역할을 합니다.
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
// 인증 전의 Authenticaion 객체를 받아서 인증된 Authentication 객체를 반환
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> var1);
}
AuthenticationManager
인증에 대한 부분은 SpringSecurity의 AuthenticationManager 를 통해서 처리하게 되는데, 실질적으로는 AuthenticationManager에 등록된 AuthenticationProvider 에 의해 처리됩니다. 인증이 성공하면 Authentication의 아래 생성자로 인증이 성공한(isAuthenticated=true) 객체를 생성하고 SecurityContext에 저장합니다. 인증을 유지하기 위해서 세션에 보관하며 인증이 실패한 경우 AuthenticationException을 발생시킵니다.
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities)
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
AuthenticationManager를 implements 한 ProviderManager는 실제 인증 로직을 갖고있는 AuthenticationProvider List를 갖고있고 for문을 통해 List에서 AuthenticationProvider 의 supports() 가 참인것을 찾고 authenticate()를 실행하여 인증처리를 합니다. 따라서 실제 인증자체는 AuthenticationProvider의 authenticate() 를 통해 일어나고 supports()는 지원여부를 파악합니다.
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,
InitializingBean {
public List<AuthenticationProvider> getProviders() {
return providers;
}
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//for문으로 모든 provider를 순회하여 처리하고 result가 나올 때까지 반복한다.
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
....
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
}
....
}
throw lastException;
}
}
AuthenticationProvider를 직접 구현하여 만든 CustomAuthenticationProvider를 이러한 ProviderManager에 등록하는 방법은 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter를 상속해 만든 SecurityConfig에서 할 수 있습니다. WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter의 상위 클래스에서는 AuthenticationManager를 가지고 있기 때문에 우리가 직접 만든 CustomAuthenticationProvider를 등록할 수 있습니다.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Bean
public CustomAuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider() throws Exception {
return new CustomAuthenticationProvider();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider());
}
}
UserDetails
인증에 성공하여 생성된 UserDetails 객체는 Authentication 객체를 구현한 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 생성하기 위해 사용됩니다.
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}
UserDetailsService
UserDetilsService 인터페이스는 UserDetails 객체를 반환하는 메서드를 갖고있습니다. 일반적으로 이를 구현한 클래스에서 UserRepository 를 주입받아 DB와 연결하여 처리합니다.
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String var1) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
Password Encoding
아래오 같이 앞서 작성했던 SecurityConfig에 추가하여 패스워드 암호화에 사용될 PasswordEncoder 구현체를 지정할 수 있습니다.
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
GrantedAuthority
현재 사용자(principal) 가 가지고 있는 권한을 의미합니다. ROLE_ADMIN, ROLE_USER 처럼 ROLE_* 형태로 사용합니다.
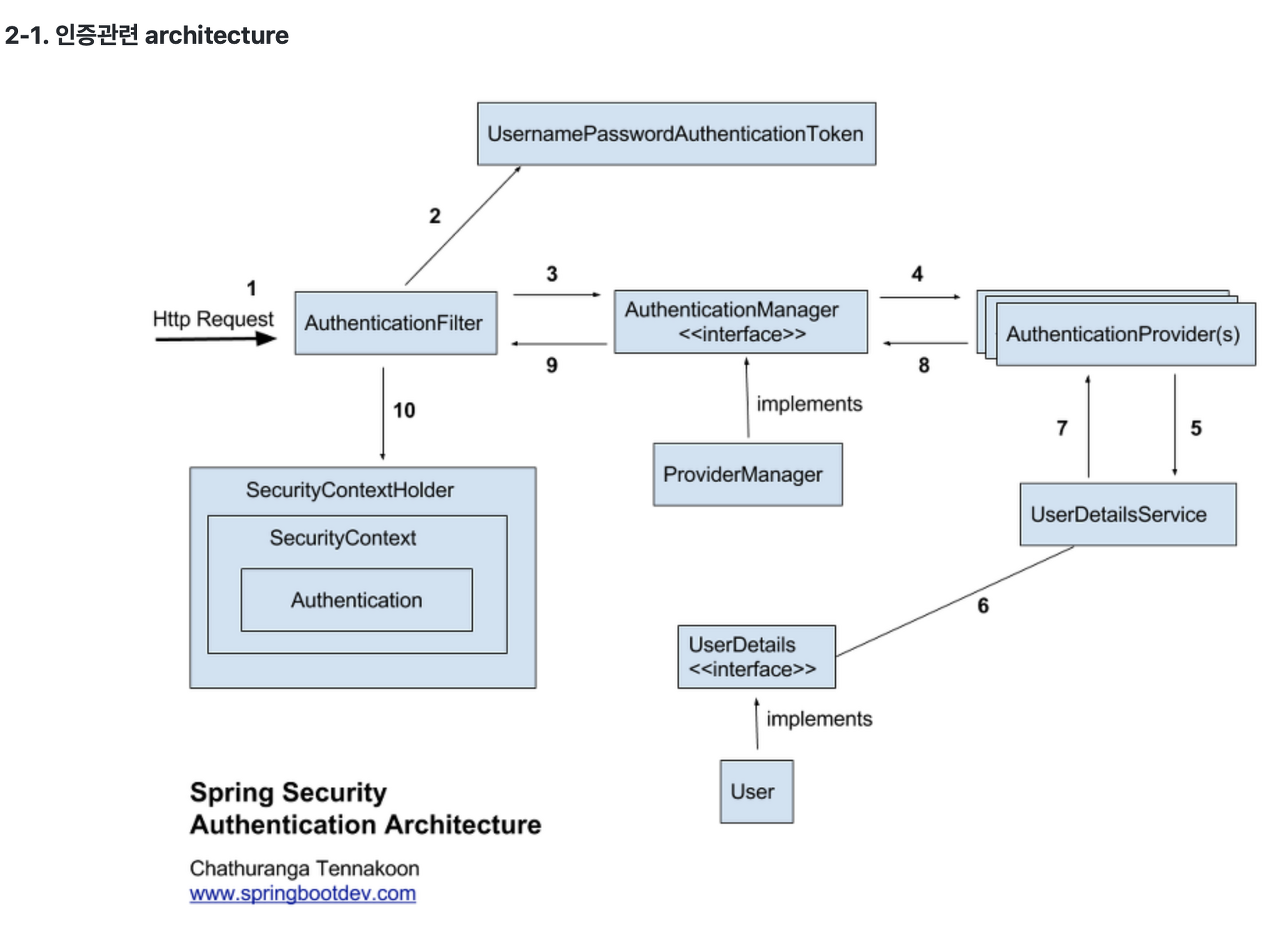
- 사용자가 아이디, 비밀번호로 로그인을 요청함
- AuthenticationFilter로 요청이 들어오게 되고, 아이디와 비밀번호를 기반으로 아직 인증되지 않은 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 생성한다.
- 생성된 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 AuthenticationManager 에 전달한다.
- AuthenticationManager 내부 authenticate(Authentication authentication) 가 실행되는데 실제 인증과정에 대한 로직은 AuthenticationProvider 에 있다. 때문에 AuthenticationProvider 의 supports(Class<?> authentcation) 으로 AuthenticationProvider List 중에서 해당 Authentication 처리 가능한 AuthenticationProvider 를 찾고 처리가능한 AuthenticationProvider 를 찾았으면 AuthenticationProvider 의 authenticate() 메서드 호출한다.
- 아직 인증되지 않은 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 받아서 내부의 정보(id, pw,,,) 를 얻는다. 인증된 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 생성하기 위해 UserDetailService 의 loadUserByUsername(String var) 를 호출한다.
- loadUserByUsername() 메서드를 통해서 UserJpaRepository 를 통하여 Optional
를 찾아오고 UserDetails 을 반환하기 위해 User 를 UserDetails 구현체로 변환한다. - 변환된 UserDetails 구현체를 반환한다.
- 획득한 UserDetails 구현체를 이용하여 인증된 UserPasswordAuthenticationToken 을 생성하고 반환한다.
- 넘어온 UserPasswordAuthenticationToken 를 반환한다.
- 토큰을 사용하지 않고 세션을 활용하는 지금과 같은 경우CustomLoginSuccessHandler 에서 SecurityContextHolder -> SecurityContext 에 UserPasswordAuthenticationToken 를 저장한다. 나중에 사용자의 정보를 꺼낼 경우에도 SecurityContextHolder 의 context에서 조회하면 된다.
reference
댓글남기기