순열
순열(nPr)
순열이란 n 개의 값 중에서 r 개의 숫자를 순서를 고려해서 뽑는 경우를 말한다.
[1,2,3] 의 경우 3P2 = (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2) 로 6개 이다.
순열에서 (1, 2) 와 (2, 1) 처럼 순서가 다르면 다른것이 된다.
참고
nPr = n! / (n-r)!
5P2 = (5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1) / (3 x 2 x 1) = 5 x 4 = 20
1. Swap 을 이용한 순열
배열의 위치를 변경하는 swap() 메서드를 직접 만들고 배열의 첫 값 부터 순서대로 모든 값 들을 하나씩 swap 한다.
depth 를 기준 인덱스로 하여 depth 보다 작은 인덱스의 값들은 고정하고 depth 위치의 원소와 depth 이상의 인덱스의 원소들을 swap 한다.
아래 그림처럼 depth = 1인 경우 1보다 작은 0의 위치한 값들은 고정이 되고 인덱스 1인 값과 1이상의 인덱스의 원소값들의 순서가 바뀌는 것을 볼 수 있다.
depth: 1 <-> index: 1(자기 자신이라 교환해도 그대로), index: 2
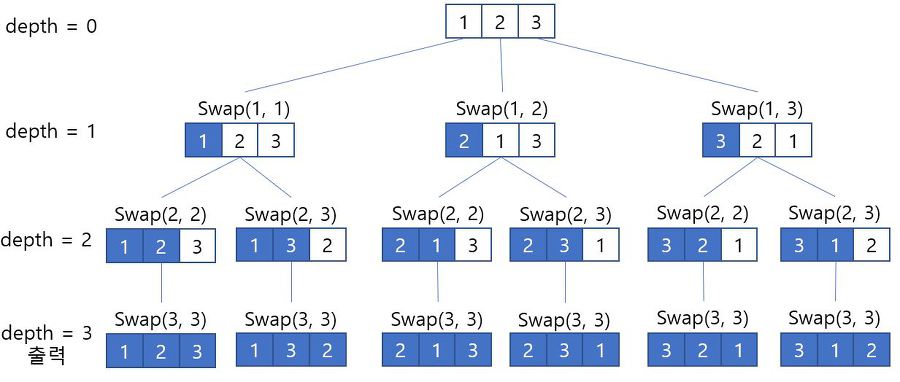
- arr : 대상 배열
- depth : depth 를 1씩 증가시키며 범위를 줄여나간다. r을 직접 줄이는게 아니라 depth 변수로 r은 그대로 두며 범위를 좁혀나감
- n, r : n개 중 r개 선택(nPr)
depth == r 인 경우가 다 뽑은 것으로 종료
//1. Swap 함수를 이용해 구현 - 순서 없이 n 개중에서 r 개를 뽑는 경우, nPr {1, 2, 3}, 0, 3, 3
public static void permutation1(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) {
print(arr, r);
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, depth, i);
permutation1(arr, depth + 1, n, r);
//1,3,2 로 변경된 걸 다시 1,2,3으로 변경하는 식으로 처음 상태로 만들어서 모든 경우를 확인한다.
swap(arr, depth, i);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int depth, int i) {
int tmp = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
}
public static void print(int[] arr, int r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
Result
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 2 1
3 1 2
이 방식으로 구현한 경우 순열들의 순서가 보장되지 않는다.
3 개의 숫자들 중 3 개의 값을 뽑는 순열을 만들 때(3P3)
[3, 1, 2]
[3, 2, 1]
위 순서대로 나오는게 순서가 보장되는 거라면 (앞에서 부터 오름차순)
swap을 이용한 구현은 아래처럼 순서가 보장되지 않는다.
[3, 2, 1]
[3, 1, 2]
구현2) visited 배열을 이용한 순열
- arr : 뽑을 대상 배열
- output : 뽑힌 r 개의 값들이 있는 배열
- visited : 중복해서 뽑지 않도록 뽑았다는 것을 체크하기 위한 배열
DFS를 돌면서 모든 인덱스를 방문하여 output에 값을 넣는다.
output에 값을 넣을때 뽑았다는 것을 체크할 수 있도록 visited 에 true를 넣는다.
swap 으로 구현할 때 처럼 depth 를 1씩 증가시키며 범위를 좁혀나간다.
depth == r 인 경우가 다 뽑은 것으로 종료
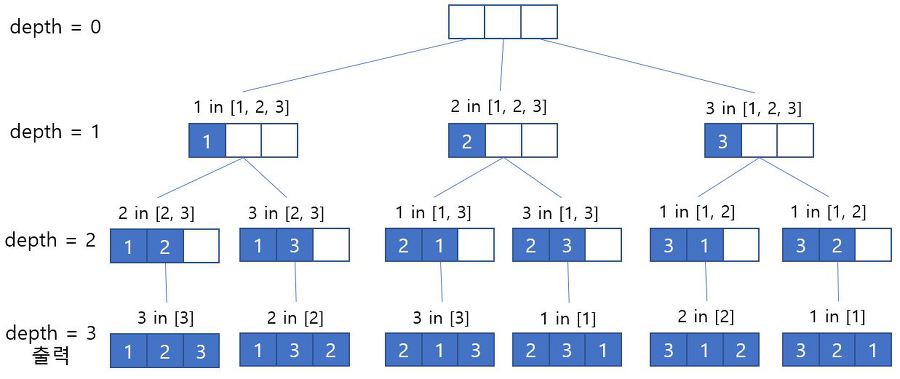
//2. DFS를 이용해 구현 - 순서를 지키면서 n 개중에서 r 개를 뽑는 경우
//output: 출력용 배열
public static void permutation2(int[] arr, int[] output, boolean[] visited, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) {
print(output, r);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i] != true) {
visited[i] = true;
output[depth] = arr[i];
permutation2(arr, output, visited, depth + 1, n, r);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void print(int[] arr, int r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
전체 코드
/**
* Permutation, 순열
* nPr
*/
public class Permutation {
//1. Swap 함수를 이용해 구현 - 순서 없이 n 개중에서 r 개를 뽑는 경우, nPr {1, 2, 3}, 0, 3, 3
public static void permutation1(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) {
print(arr, r);
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, depth, i);
permutation1(arr, depth + 1, n, r);
//1,3,2 로 변경된 걸 다시 1,2,3으로 변경하는 식으로 처음 상태로 만들어서 모든 경우를 확인한다.
swap(arr, depth, i);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int depth, int i) {
int tmp = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
}
//2. DFS를 이용해 구현 - 순서를 지키면서 n 개중에서 r 개를 뽑는 경우
//output: 출력용 배열
public static void permutation2(int[] arr, int[] output, boolean[] visited, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) {
print(output, r);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i] != true) {
visited[i] = true;
output[depth] = arr[i];
permutation2(arr, output, visited, depth + 1, n, r);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void print(int[] arr, int r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("-------- 1. Swap ---------");
permutation1(arr, 0, n, 3);
int[] output = new int[n];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
System.out.println("-------- 2. DFS ---------");
permutation2(arr, output, visited, 0, n, 3);
}
}
참고: https://bcp0109.tistory.com/14
댓글남기기